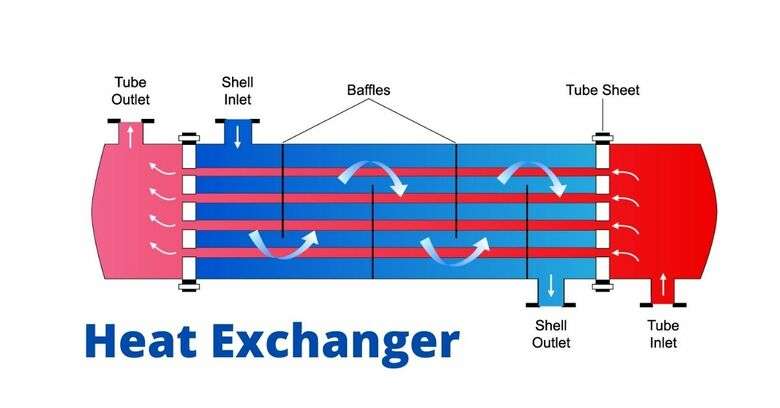
Heat exchanger are one of the most common pieces of equipment found in all plants. Heat exchangers are components that allow heat transfer from one fluid (liquid or gas ) to another fluid.
Heat exchangers are equipment that transfer or exchange heat between two liquids without mixing. All heat exchangers feature an enclosure that separates the two fluids and permits simultaneous heat transfer. They come in various designs based on their configuration, the application, the space, and the fluid circulation through the system.
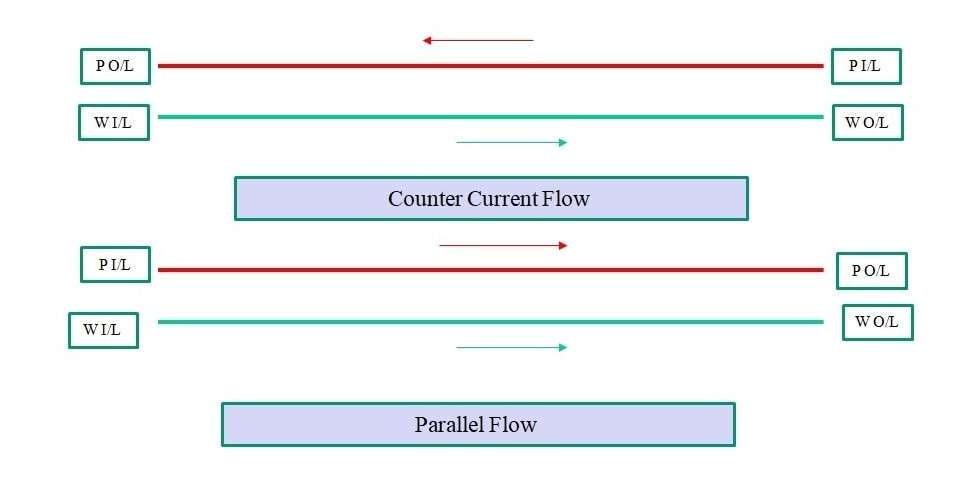
Flow arrangement in Heat Exchanger
Some common Heat Exchanger Terms
- Tube side: Inside the tubes
- Shell Side: Outside the tubes, between the tube and the shell.
- Tube Sheet: A thick plate provided with holes (one per tube) in which the tubes are fixed.
- Tube Bundle: Consists of tubes, tube sheet and baffle plate.
- Shell: A cylinder of plate in which the tube bundle is placed.
Heat Exchanger Classification
Type of Heat Exchanger
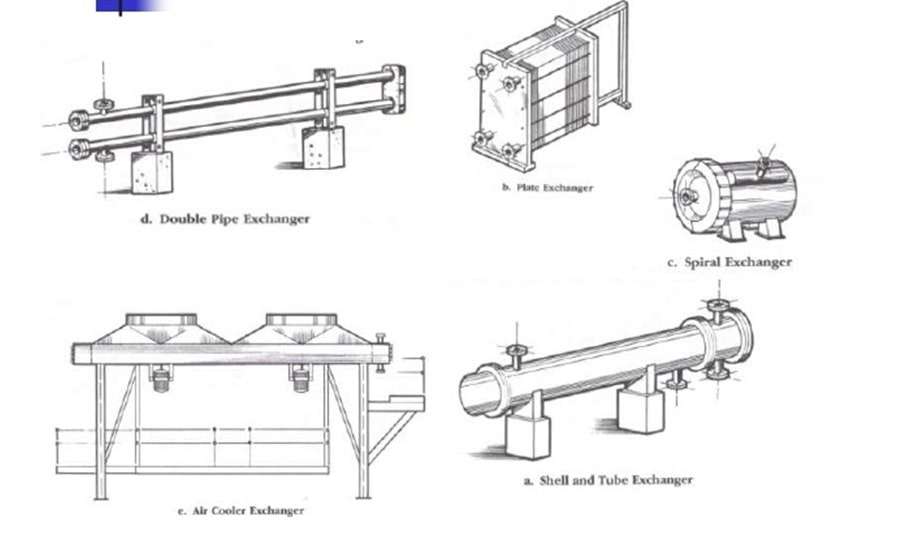
a) Heat Exchanger Shell and Tube
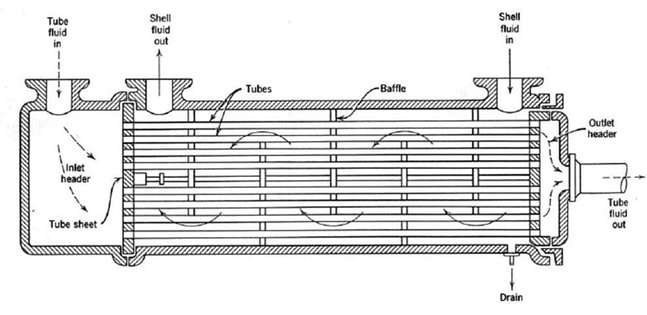
Shell and Tube Heat exchangers are the most important type of Heat exchanger. It is used in almost every type of industry. A shell and tube heat exchanger has a set of tubes bundled in a container, it is called a shell.
When fluid passes inside the tube than it is called the tube side fluid and when the fluid passes on the outside of the tube is the shell side fluid.
b) Double pipe Heat Exchanger
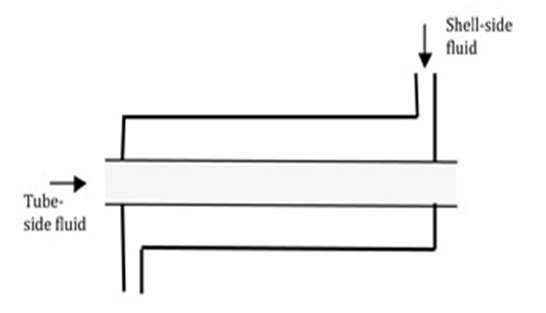
A double-pipe heat exchanger can be one of the fundamental types of exchangers with a flexible design. There are two kinds of parallel flow or counterflow.
The double pipe heat exchanger has a small diameter pipe that is surrounded by a large diameter pipe. The fluid flow inside the small diameter pipe and water flow outside.
c) Heat exchanger plate type
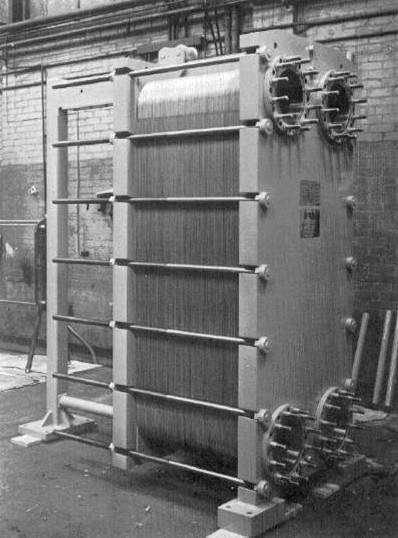
The plate heat exchanger is used metal plates to transfer heat from two liquids. It has a benefit over a traditional heat exchanger because the fluids will be exposed to a larger area across the plates. This makes it easier to transfer heat and significantly enhances the speed of temperature changes.
d) Air Cooled Heat Exchanger
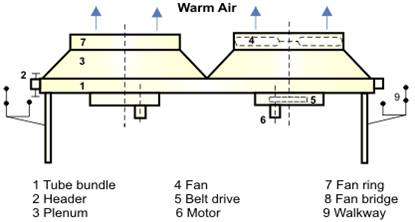
Air-cooled heat exchangers are typically used in industries where water isn’t readily available for cooling. Even if water sources are available, air-cooled exchangers are preferred for financial and operational benefits in a few instances.
e) Spiral Heat Exchanger
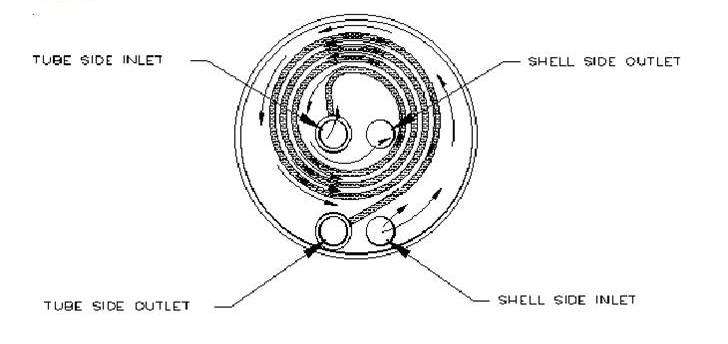
Spiral heat exchangers can be employed in all kinds of applications within the chemical process industry.
A typical tube and shell design may not be efficient in many challenging applications in which plugging and fouling can be an issue.
While a spiral heat exchanger is usually more expensive initially, it can also provide lower cost over the life of the unit due to a lower fouling rate and simple maintenance.